We believe In…

Human centred design
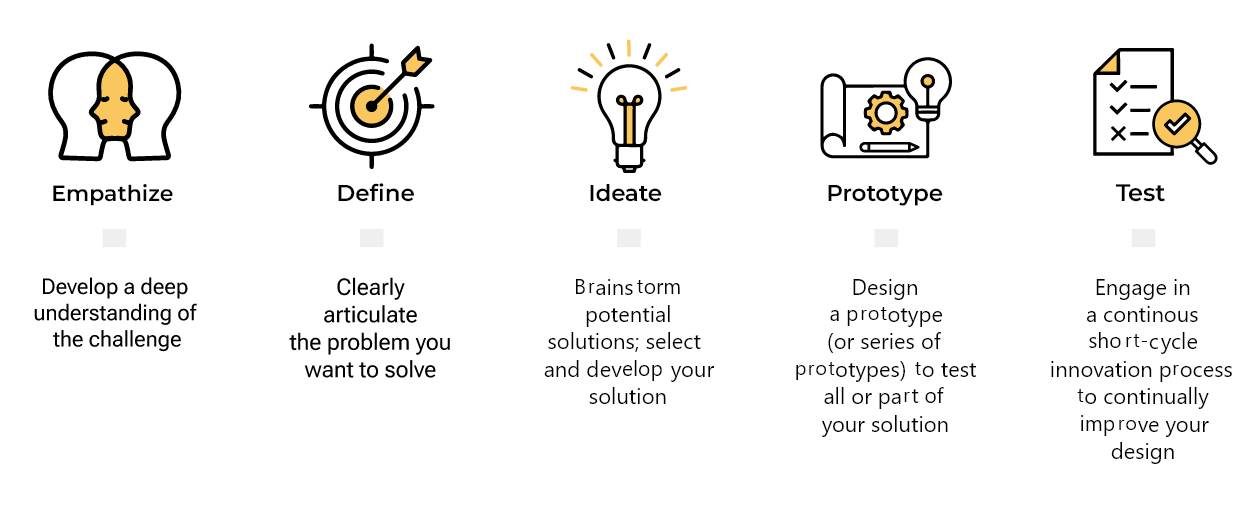
Human-centered design is a problem-solving approach that puts people at the center of the design process. It involves understanding the needs, wants, and behaviors of the people who will use or interact with the product, service, or system being designed.
Human-centered design involves several stages, including research, ideation, prototyping, and testing. During the research phase, designers gather insights about the users and their needs through methods such as interviews, surveys, and observation.
During the ideation phase, designers brainstorm and generate ideas that address the needs and insights gathered during the research phase. The prototyping phase involves creating low-fidelity and high-fidelity prototypes to test and refine the ideas. Finally, during the testing phase, designers gather feedback from users and iterate on the design to improve its usability and effectiveness.

Balancing people, business and technology perspectives
People perspective: Understanding the needs, wants, and behaviours of users are essential for creating a product that people will use and love. By incorporating a people perspective, designers can create products that are intuitive, accessible, and enjoyable to use.
Business perspective: It’s important to consider the business goals and constraints when designing a product. A product that doesn’t align with the company’s goals or can’t be produced efficiently may not be sustainable in the long run. By incorporating a business perspective, designers can create products that are both user-friendly and financially viable.
Technology perspective: Understanding the technical capabilities and limitations is important for designing a product that can be built and maintained effectively. By incorporating a technology perspective, designers can ensure that the product is feasible to develop and can be maintained and updated as needed.

Evidence based UX design
The goal of evidence-based UX design is to create digital products that are user-centered, effective, and efficient. By using evidence to inform design decisions, designers can create interfaces and products that are more likely to meet the needs and preferences of users. Some of the key methods and techniques used in evidence-based UX design include:
User research: Conducting user research through methods such as interviews, surveys, and usability testing to gather insights about users’ needs, goals, and behaviours.
Analytics: Analysing user data, such as website traffic, click-through rates, and conversion rates, to gain insights into user behaviour.
A/B testing: Conducting A/B testing to compare two different versions of a design and determine which performs better with users.
Expert reviews: Seeking feedback and input from experts in UX design, information architecture, and other related fields.
The People

Arun
Associate UX engineer

Babushekar
Associate Director

Barathkumar
Lead UX Engineer

Binu
Associate Director

Dharani
Associate UX engineer

Gopi
Senior Creative Lead

Keerthana
Associate UX engineer

Kishor
Director

Meenakshi
Associate UX engineer

Noufal
Lead UX engineer

Praveen
Associate UX engineer

Sathish
Creative Lead

Sathvi
UX engineer

Sidhardhan
Senior Creative Lead

Sumesh
Associate Creative Manager

Swetha
UX engineer